日志
[ZZ]A short introduction to IC Compiler II
| ||
A look under the hood of IC Compiler II, Synopsys’ next-generation netlist-to-GDSII implementation system.
IC Compiler II is a complete netlist-to-GDSII implementation system that includes early design exploration and prototyping, detailed design planning, block implementation, chip assembly and sign-off driven design closure. The foundation, architecture and implementation is based on novel, patented technologies and the software has been written using modern object-oriented languages and tools.
IC Compiler II, which is marketed alongside the original IC Compiler, is meant to give designers of complex ICs, at all process nodes, a ten-fold improvement in design throughput. No single feature can achieve such broad improvements in productivity. Traditional tools produce marginal improvements by applying incremental techniques to an existing architecture.
IC Compiler II benefits from the combination of a new hierarchical infrastructure enabling massive parallelism; a highly compact multi-corner and multi-mode (MCMM) architecture; next-generation design-planning; new global, analytical, and scalable optimization techniques; and global optimization approaches to clock synthesis. IC Compiler II also fits into existing design flows using industry-standard interfaces and file formats.
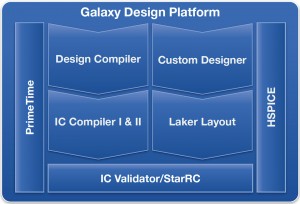
Figure 1 How the IC Compiler II physical implementation system fits into the Synopsys Galaxy Design Platform. (Source: Synopsys)
A modern infrastructure
IC Compiler II’s infrastructure has been built to handle increasingly large designs using a highly scalable data model that enables high capacity, engine efficiency and broad parallelism. Its main characteristics are:
- Object orientation, enabling the flexibility to add objects and instant access to all objects and their attributes.
- Linearly scalable data access and modification, enabling complete parallelism for engines.
- Native modeling of multi-level physical hierarchy, including multiply-instantiated blocks. This enables efficient and easy to use, very large transparent hierarchical implementation.
- Native modeling of high-level objects such as voltage areas, power domains and route corridors. This enables the engines to easily access and optimize within and across these objects.
- Modeling of design state. This brings compact snapshot creation for both design data and state, enabling fast, reliable and lossless transfer between designers.
- A change manager that monitors any changes in data, enabling robust and efficient notification for incremental analysis.
- A flexible architecture for adding and handling the increasingly large number of advanced technology rules.
- Compact modeling and representation of modes and corners for efficient analysis and optimization. This enables a much larger set of mode/corner combinations to be used throughout the flow.
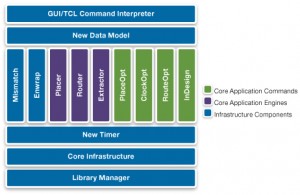
Figure 2 Simplified view of the tool architecture (Source: Synopsys)
IC Compiler II’s library manager produces a common reference library that integrates the physical, logical and timing data in a compact, fast-access database. Two powerful new library concepts are used:
- Aggregate libraries that hide the complexity of many individual reference libraries by organizing and presenting them to the tool in a well-defined search order
- Sparse/shared design and reference libraries, managed in a similar way to those underpinning distributed code development schemes, enabling collaborative design amongst a large group of designers
Native, multi-level physical hierarchy modeling enables optimization across hierarchical boundaries as all levels of the hierarchy are visible for all operations in one pass without loading the entire design in memory. This enables access and manipulation of objects at any level in the physical hierarchy in the context of the top level - a concept known as ‘multi-level transparent hierarchy’.
IC Compiler II’s timing engine has these features:
- Architected for modern designs with any number of modes and corners
- Deployment of a single, cross-flow implementation timer to deliver design convergence through placement, clock and routing
- Native support for very fast, incremental timing updates
- Highly correlated to PrimeTime, thereby reducing sign-off surprises and bringing fewer ECO iterations
- Hyper-threading, enabling fine-grain parallelism to take advantage of all available cores
Ultra-high capacity design planning
Modern designers spend a lot of the schedule in floorplanning their design to get the best quality of results (QoR). The quality of the floorplan has a profound effect on the final implementation results. With rapidly increasing design sizes, inaccurate and incomplete data at the start of the process, complex design styles and time-to-market pressures, generating a good floor-plan becomes increasingly difficult.
IC Compiler II design planning is meant to combat these challenges. Aided by the new infrastructure, IC Compiler II employs novel, adaptive-abstraction and parallel computing techniques that eliminate capacity limits.
IC Compiler II’s design planning never needs the entire design in memory to do the planning. Traditional parallel techniques suffer from quality issues due to the creation of artificial partition boundaries. IC Compiler II’s parallel design-planning techniques optimize the floorplan in the global context. New, patented algorithms are more than 10 times faster than traditional design planning techniques. These runtimes have been validated by early customers.
Early design stages come with incomplete and mismatched data. Techniques to manage such data and extract useful information from it are built into IC Compiler II’s design-planning and exploration system. New algorithms for fast congestion and timing estimation, and data-flow analysis with real-time user feedback, are integrated into IC Compiler II’s exploration flow. With ultra-fast design-planning and exploration capabilities, IC Compiler II’s design planning can analyze and optimize designs of more than 500 million instances and provide useful information to RTL designers in hours. Traditionally it has taken from a few days to a week to obtain such feedback.
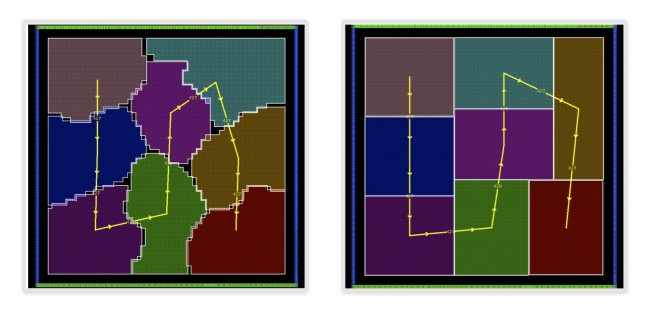
IC Compiler II’s design-planning algorithms are data-flow aware. Macro placement and block placement solutions are automatically optimized in the context of overall data flow, thereby capturing user intent and producing high-quality floorplans, as seen in Figure 3 below.
Figure 3 Data-flow driven placement and shaping (Source: Synopsys)
Repeated blocks are ubiquitous in large hierarchical designs. IC Compiler II’s design-planning engines can optimize floorplans for such designs in a global context. Engines such as block placement, macro placement, global routing, pin assignment, optimization and budgeting are all aware of the constraints imposed by repeated blocks and produce optimal results considering all such constraints. IC Compiler II’s engines automatically derive the symmetry and orientation of repeated blocks and produce floorplans with optimal data flow for such designs.
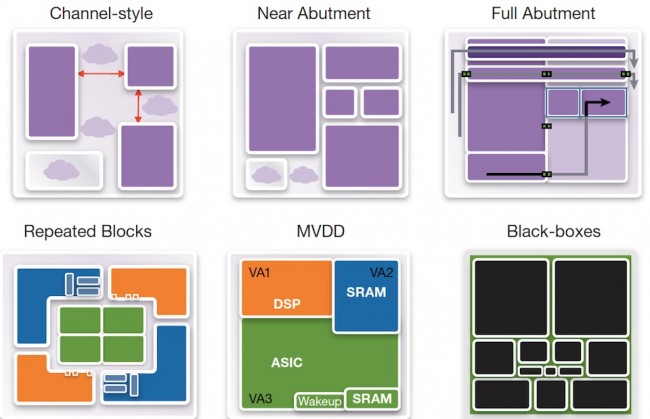
IC Compiler II’s design-planning system uniformly handles all customer design styles and flows; channeled, abutted, narrow channeled, black box, top down and bottom up. UPF is automatically handled throughout the flow with full support for golden UPF flows.
Figure 4 Six example ways to plan a complex IC supported in IC Compiler II (Source: Synopsys)
Analytical optimization
Physical synthesis and optimization is an integral part of implementation flow. Optimization is becoming a major bottleneck for large designs, because of their growing size, increasing number of modes and corners, complex multi-voltage schemes, increasing cost functions and congestion challenges.
Traditional optimization schemes have relied on highly localized, iterative optimization on critical paths. Though these schemes have worked well thus far, a fresh approach is needed to keep up with increasing complexities.
IC Compiler II’s optimization strategies include:
- Global optimization that enables the optimization engine to manipulate large chunks of logic simultaneously. Local schemes tend to fall into local minima, thereby ignoring opportunities to produce better designs using global optimizations and incurring long runtimes on hard-to-close designs.
- Analytical optimization using fast, parallel numerical solvers
- Innovative algorithms that optimize across all modes and corners at once. IC Compiler II’s optimization enables the addition of increasing modes and corners without significant overhead. This enables faster convergence through the flow.
- Newly developed, accurate interconnect-topology, layer and congestion modeling earlier in the flow, using the Zroute global-routing engine. This is delivered with low performance penalties, resulting in faster convergence.
- Highly scalable parallel optimization. Due to the global nature of timing paths and algorithms dominated by memory access, traditional physical synthesis techniques have suffered from low multi-processor scalability. IC Compiler II’s algorithms take a different approach and so are faster on a single core, and scale well with more processors.
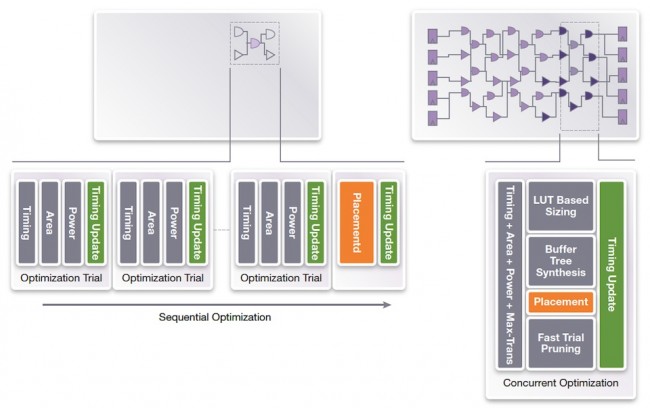
- Concurrent optimization of key design metrics such as timing (setup and hold), power, congestion, logical and physical DRCs and area. This results in monotonic improvements across all metrics throughout the flow.
- Concurrent placement, buffering, sizing, gate transformations and interconnect optimization for optimal QoR with fast turn-around times.
Figure 5 Comparison of classical optimization and IC Compiler II’s optimization approach (Source: Synopsys)
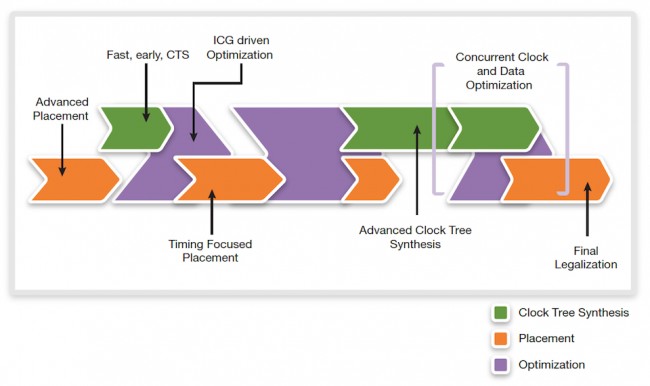
With accurate modeling of clock structures, including clock gates earlier in the flow, and new algorithms for concurrent clock and data optimization, IC Compiler II improves the correlation of results before and after CTS. This reduces the need for re-optimization of paths after CTS. These techniques and overall flow, shown in Figure 6, improve runtime and QoR for high-performance designs.
Figure 6 Convergent pre-optimization flow (Source: Synopsys)
The combination of the new infrastructure, very fast timing and extraction engines, and the new optimization techniques in IC Compiler II have already demonstrated an order of magnitude improvement in design throughput for a number of customers.
Clock synthesis and optimization
The robust synthesis of clocks has become increasingly complex and time consuming with the rapid increase in the number of sequential elements, the growing number of clocks in a design, increasing numbers of modes and corners, stringent skew requirements, skew sensitivity to gate and interconnect delay variations, and the usage of clock gates for power reduction.
Common clock synthesis algorithms suffer from serious runtime problems and generate un-optimized trees that consume too much power, a major issue for today’s designs, especially for mobile applications.
IC Compiler II’s clock synthesis uses a novel approach that formulates all clocks for all modes and corners as a network flow problem, which is solved by a new patented algorithm. The main characteristics of IC Compiler II’s clock synthesis solution are:
- Simultaneous handling of all clocks across all modes and corners, resulting in variation-tolerant clock trees.
- Maximal use of path sharing to minimize on-chip-variation effects.
- Optimal clock-gate insertion and minimized clock buffer usage for dynamic power reduction.
- Automatic clock exception generation that minimizes or eliminates manual intervention.
- Optimal clock feedthroughs over voltage areas, which eliminates long detours.
- Clock routing using Zroute global routing technology, which helps maintain skew and timing correlation throughout the flow.
- Clock debugging and analysis through abstract clock graphs, which abstracts clock information and presents leveled and latency-based clock data for users to visualize and analyze.
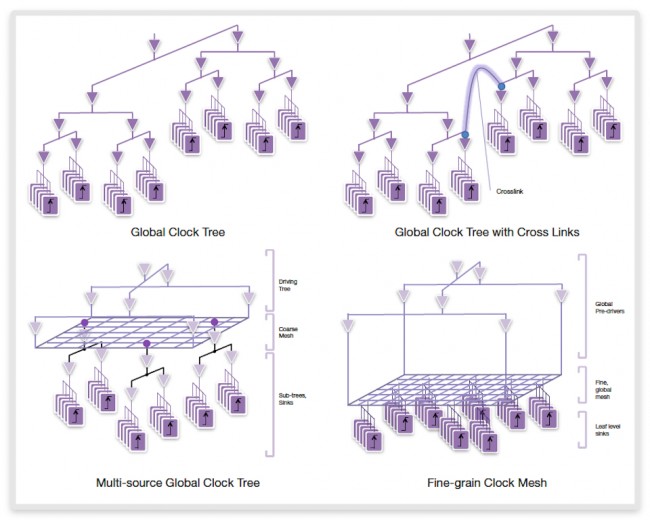
IC Compiler II’s clock engine architecture unifies regular clock tree and mesh synthesis technologies, providing one environment for various clock methodologies. The mesh and tree engines work together and are used in the same way. This enables customers to generate hybrid mesh/tree structures, including the multi-source and cross-linked clock structures that are often used in high-speed and low-power designs.
Figure 7 New clock architecture enables unified approach to handle all styles of clock structures (Source: Synopsys)
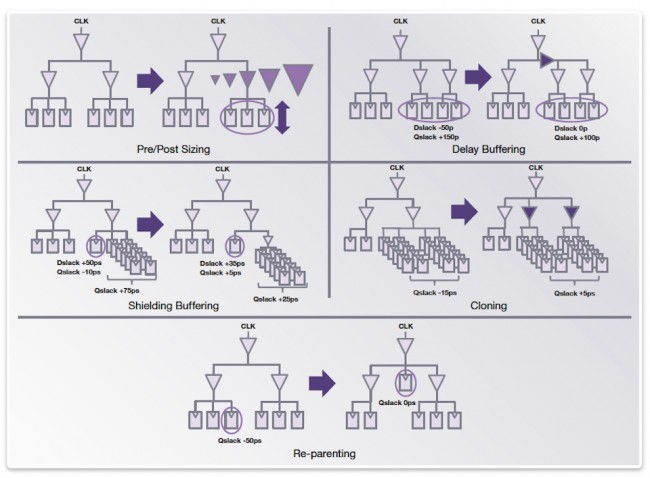
IC Compiler II’s clock engine is integrated with the data-optimization and placement engine that can concurrently optimize clock and data paths. Clock-skew adjustment and data-path synthesis are simultaneously costed to obtain the best solution for timing, area, power, DRC and routability. IC Compiler II’s concurrent clock, data and placement optimization also optimizes WNS and TNS simultaneously.
Figure 8 A novel set of techniques is deployed locally and globally on the clock tree during concurrent clock and data optimization (Source: Synopsys)
With an advanced infrastructure, a unified architecture for clock and data-path optimization and new techniques for clock synthesis, IC Compiler II’s clock solution can deliver more than 5X speedup for clock synthesis, better timing and lower power. This has been demonstrated on multiple production tape-outs.
Core technology support
IC Compiler II uses the core placement engine, as well as the Zroute routing engine from IC Compiler. These are both enhanced with fast data access from the new scalable infrastructure. By sharing these two engines with IC Compiler, all of the investment made for supporting both established and emerging nodes is reused. This includes support for all of the latest rules for double patterning as well as the many physical placement constraints seen when using finFETs.
Summary
IC Compiler II is a new physical design tool that allows complete netlist- to-GDS II implementation. With a modern infrastructure, new, patented techniques for design planning, optimization and clocking, IC Compiler II delivers an order of magnitude productivity improvement over current solutions. IC Compiler II has been used for multiple production tape-out designs at major customers doing designs at both established and emerging nodes. IC Compiler II was released in production in July 2014.
Further information
Visit Synopsys’ dedicated IC Compiler II microsite for more details.
Detailed white papers:
Author
Neeraj Kaul is a group director of R&D at Synopsys leading IC Compiler II product development. Kaul has spent more than 20 years serving the EDA industry in the areas of physical design and implementation, placement, CTS, routing, floorplanning, simulation, timing and functional verification, optimization and abstraction. Kaul holds a PhD in electrical and computer engineering, has published 10 conference and four journal papers, and holds four US patents.

 /1
/1 

 eetop公众号
eetop公众号 创芯大讲堂
创芯大讲堂 创芯人才网
创芯人才网