日志
时钟树优化与有用时钟延迟简介
热度 1|
时钟树优化与有用时钟延迟在 “后端时序修正基本思路” 提到了时序优化的基本步骤。其中,最关键的阶段就是时钟树建立。基本的优化都优先在数据路径上进行,并且希望路径尽量的短,最好在一个时钟周期之内。当然,如果考虑输入、输出延迟,收敛悲观因素,库的建立时间,与时钟不确定性,以及不同时钟沿触发等因素,这个要求还要进一步的压缩,这些将在以后陆续进行讨论。
通常,我们希望时钟树偏差(clock tree skew) 越小越好,目标为零。所以,在建立时钟树(CTS)之前,我们首先将时钟设定为理想时钟。这样的好处是,优化数据路径时,不会对时钟路径有额外的修改。而且,因为排除了时钟的影响,可以看到最终优化的结果,是否能够满足时序的要求。如果不满足,最要考虑的就是数据路径组合逻辑是否太多,导致延迟过长。其他,可以估计一下RC延迟所占的比例,比如15%左右,过长时,检查是否路径逻辑单元之间是否间隔的太长等等。不过,本
文重点要讨论的是,路径过长时,如何通过增加有用时钟延迟(useful skew) 来达到时序的满足。
IC compiler 有这样的命令 skew_opt ,还有其两次流程(two pass)可供参考。
阅读过本文后,我相信大家可以大致了解其工作的基本思路。
如果流程不正确,skew_opt 可能花费过长的运行时间,而且,不能达到预期的效果。如果我们清楚其中的原理,就可以更好,更自由的运用与发挥。
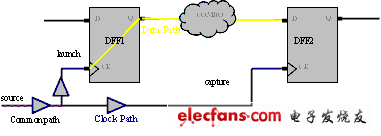
在不要考虑过多的情况下,如图,在理想时钟前提下,时序无法满足,即slack < 0 。原本我们可以做:
1,最短化数据路径,
2,提前启动时钟路径,
3,推迟捕获时钟路径。
因为选项1,我无法压缩它,现在我可以做的,就只有选项2和3了。
以选项3为例,目标为加长捕获时钟路径:
set slack [get_attr [get_timing_path] slack]
set_clock_tree_exceptions
-float_pin_max_delay_rise $slack
-float_pin_min_delay_rise $slack
-float_pins $capture_clock_pin
以上是icc 命令的范例,大体上表达将小于零的slack 以时钟特例的形式赋给捕获时钟路径在寄存器的时钟脚位。这样,icc在进行时钟树综合的时候,就会有意在捕获路径上增加多的延迟单元,起到人为的偏移,从而实现用户的意图。
当然, skew_opt 中,还有运用set_clock_latency和balance_group 来辅助时钟树平衡,以达到更好的效果。
clock skew: the difference between the time clock signals arrive at the clock sinks excluding ignore pins(clock sinks include the CK pin of sequential cells, such as transparent latches, flip-flops, ICG cells, and memory blocks, and ignore pins include explicit ones and implicit ones, such as output, pins without timing info, etc )
global skew: the clock skew between all the valid end points of the clock tree, no matter those points are logically/physically adjacent or not
local skew: only count the skwe when the two points are adjacent
useful skew: when setup/hold violation happens, we can adjust the arrival time of clock signals to meet the timing constraint. this technique is not so useful when on-chip-variation become more and more significant.

 /1
/1 

 eetop公众号
eetop公众号 创芯大讲堂
创芯大讲堂 创芯人才网
创芯人才网